Sponsored Content
Li-ion batteries and pumped storage offer different approaches to storing energy. Both deliver energy during peak demand; however, the real question is about the costs.
A scientific study of li-ion batteries and pumped storage looks at the raw material costs needed to build each, as well as their long-term carbon footprint for the construction/installation and continued operation.
The study provides clarity about both the short- and long-term economic and environmental impacts of the two storage options. Results can be used to ensure climate goals are not jeopardized by a lack of information and the underutilization of energy storage technologies.
The Deep Dive
The balancing of electrical loads and generation is an important challenge for electric power systems shaped by renewable energy sources. In this context, large-scale storage systems as a temporal flexibility option contribute to the balancing process by participating in portfolio management, energy-only markets, as well as system reserve markets. As renewables — such as wind, solar and hydro — continue to make up a larger portion of the grid, storage is needed to allow for the delivery of those resources when they are most needed. Without additional large-scale electrical energy storage, the strain on transmission grids in the United States will continue to increase as user demand and energy consumption grow.
In recent years, battery storage systems have experienced a tremendous ‘hype’ in public discussions due to technological innovation and a significant cost decrease. As a result, several new stationary battery storage systems, in the order of magnitude of hundreds of megawatt hours, have been constructed during the last decade.
However, the question still remains whether the falling costs of stationary battery storage can be competitive with a well-established technology, such as pumped storage hydropower.
We’ve seen uncertain market environments in combination with high investment costs and long-term amortization periods discourage investors from developing new pumped-storage plants.
Therefore, a scientifically justified analysis of these two different storage options was necessary in order to provide clarity and ensure that climate goals are not jeopardized by a lack of information and the underutilization of energy storage technologies.
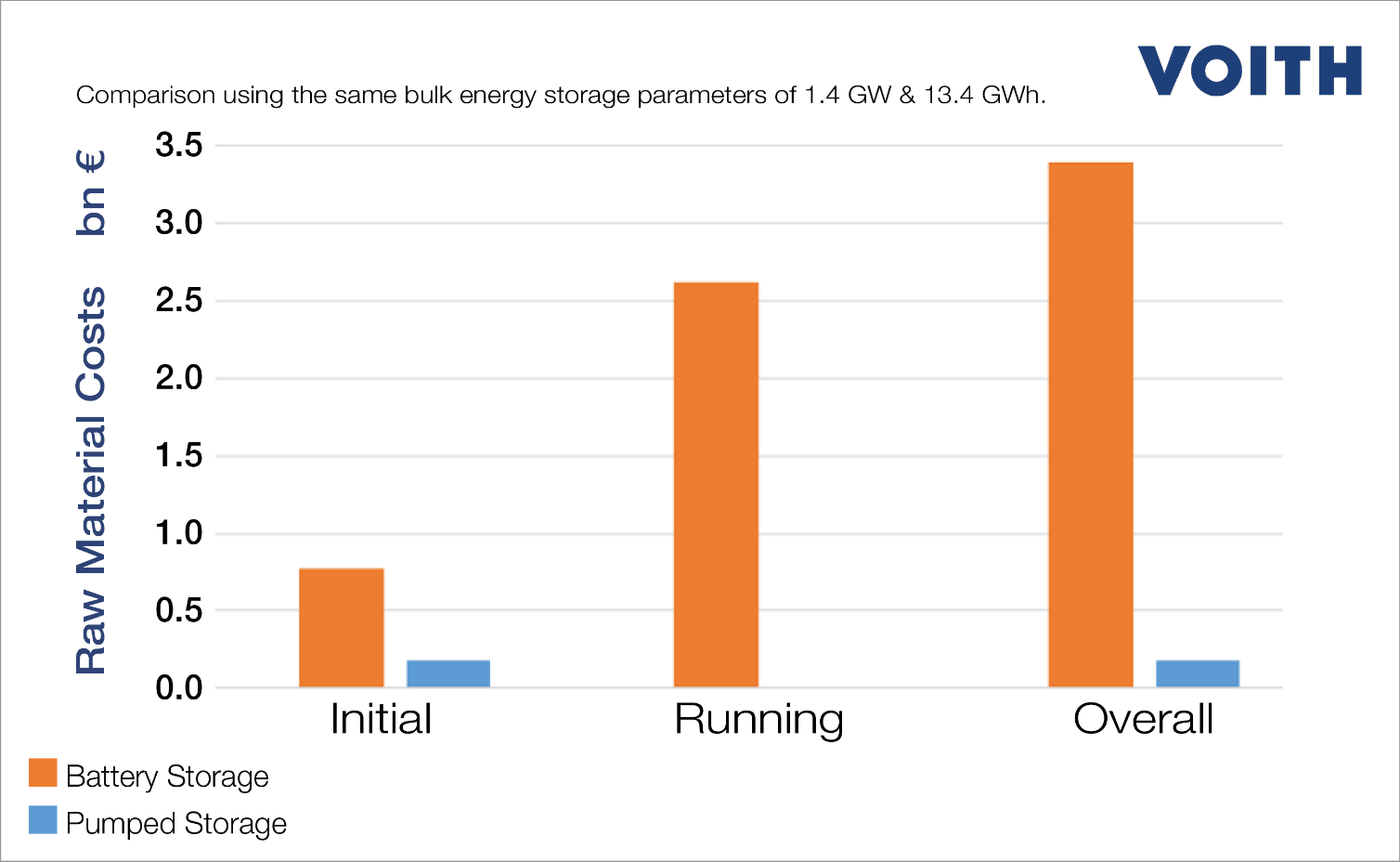
The goal of this study was to compare a stationary battery storage system and a pumped storage plant system, with a focus on key economic and environmental indicators while considering the same bulk energy storage parameters: 1.4 GW and 13.4 GWh.
It is evident that both of these systems require completely different types and quantities of resources, leading to substantial differences in their specific raw material costs. For each technology, this study compares the:
- specific raw material costs during the installation phase
- lifetime raw material requirements and costs
- lifetime investment costs
- land requirements
- carbon footprints as an indication of the environmental impact